pelvic floor dyssynergia icd 10
Contraction of the pelvic floor or urethral sphincter. Anismus that has a behavioral cause could be viewed as having similarities with.
A significant number of patients will report having had issues since.

. Biliary K838 bladder sphincter N3644 cerebellaris myoclonica Hunts ataxia G111. Your pelvic floor includes muscles and connective tissue that support your bladder rectum and other pelvic organs. However the best thing to do is query provider for clarification concerning whether condition is Neurogenic Neuromuscular or both.
Dyssynergic defecation is a condition that affects the pelvic floor muscles. Dyssynergic defecation occurs when the pelvic floor muscles are unable to coordinate with the surrounding. 59655 Detrusor sphincter dyssynergia N3644 Muscular disorders of urethra 59780 Urethritis N342 Other urethritis 1100 Wayne Ave Suite 825.
So when on the toilet the pelvic floor muscles are creating a serious kink on the rectum and its very difficult to push the. In this manuscript we will review the physiology urodynamic diagnostic techniques and therapeutic treatment options for DSD in the neurogenic bladder patient. Alphabetical List of Common ICD-10 Codes for Pelvic Rehab Providers.
Part of ICD-10 CM is the. Pelvic floor dyssynergia falls into the Rome IV criteria of a functional defecation disorder. Urogynecology ICD-9 to ICD-10 Crosswalks ICD 9 Code.
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM. Defecation Dyssynergia is most commonly due to the inability of the pelvic floor or anal sphincter muscles to relax during defecation. Constipation due to pelvic floor outlet obstruction.
Pelvic muscle wasting. Subsequently several terms have been used to describe this entity including anismus 2 pelvic floor dyssynergia 3 obstructive defecation 4 paradoxical puborectalis contraction 5 pelvic outlet obstruction 6 and spastic pelvic floor syndrome. 556 Signs and symptoms of musculoskeletal system and connective tissue without mcc.
The pelvic floor is composed of a group of muscles that span the underlying. Convert M9905 to ICD-9-CM. It is marked by the failure of pelvic floor muscles to relax or a paradoxical contraction of the pelvic floor muscles with defecation.
Pelvic floor muscles support organs within the pelvis and lower abdomen maintain continence allow for bladder and bowel emptying and contribute to sexual arousal and orgasmic. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 BillableSpecific Code. M9905 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of segmental and somatic dysfunction of pelvic region.
When you have pelvic floor dyssynergia pelvic dyssynergia the muscles in your pelvic floor become uncoordinated. 392 Esophagitis gastroenteritis and miscellaneous digestive disorders without mcc. In constipation the pelvic floor muscles are tight and overactive and do not know how to relax.
The pelvic floor muscles do this by supporting organs such as the rectum uterus and bladder. Convert K5902 to ICD-9-CM. ICD-10 Common Codes for Pelvic Rehab Providers Listed Alphabetically Abdominal distension gaseous Bloating Tympanites abdominal intestinal R140 Abdominal pain R109 more specific codes available as right and left upper or lower quadrants Anal spasm Proctalgia fugax K594 Bladder pain R3989.
Chronic constipation affects 11-18 of the population with a female-to-male ratio of almost 21. I would go with N319-Neuromuscular dysfunction of bladder unspecified. Fecal impaction K5641 incomplete defecation R150 Constipation unspecified K5900.
7 Pelvic floor is a complex muscular apparatus that serves three important functions namely. Often times a paradoxical contraction may occur when attempting to relax the pelvic floor muscles further inhibiting bowel function and emptying. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N8189 became effective on October 1 2021.
Coccygodynia See Sacrococcygeal disorders not elsewhere classified M533. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R102 became effective on October 1 2021. It can occur in both children and adults and in both men and women.
This is the American ICD-10-CM version of R102 - other international versions of ICD-10 R102 may differ. Anismus or dyssynergic defecation is the failure of normal relaxation of pelvic floor muscles during attempted defecation. These are muscles located in the lower abdomen that allow bowel movements to pass normally.
There are 3 terms under the parent term Dyssynergia in the ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index. When you sit on the toilet the pelvic floor muscles should relax so that you are able to empty your bladder or bowel. An example of anorectal dysfunction that can contribute to constipation is a condition called Pelvic Floor Dyssynergia also referred to as anismus.
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index is designed to allow medical coders to look up various medical terms and connect them with the appropriate ICD codes. The ICD-10-CM code M9905 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like abnormal. It can be caused by physical defects or it can occur for other reasons or unknown reasons.
A paradoxical contraction is when the pelvic floor muscles contract. R102 is a billablespecific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N8189 - other international versions of ICD-10 N8189 may differ.
Also code additional if documented identifying urinary incontinence N393-N394X series. ICD-10-CM K5902 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Groups MS-DRG v 390. This makes it difficult to have a bowel movement.
ICD-10-CM M9905 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group s MS-DRG v390. Somatic dysfunction of pelvic region. Detrusor sphincter dyssynergia DSD is the urodynamic description of this neurologically induced bladder outlet obstruction.
All-encompassing terms such as pelvic floor dyssynergia or pelvic outlet obstruction imply that this problem affects most of the pelvic floor and possibly all of its functions. Of patients with chronic constipation 25-50 of them have pelvic floor issues. 555 Signs and symptoms of musculoskeletal system and connective tissue with mcc.
N8189 is a billablespecific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. N8184 is a billablespecific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The code M9905 is valid during the fiscal year 2022 from October 01 2021 through September 30 2022 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
Pelvic muscle wasting Cervical stump prolapsed Other female genital organ prolapsed 61801. The pelvic floor is a dome-shaped muscle complex with contraction occurring in 3 planes26 Its complex actions include tightening lifting squeezing and relaxing. Although some overlap has been described among patients with urinary obstruction and constipation 10 most constipated patients do not report sexual or urinary symptoms 11.
These muscles tighten contract to prevent stool from leaking. 391 Esophagitis gastroenteritis and miscellaneous digestive disorders with mcc.

320 Male Pelvic Floor Dysfunction The Great Masquerader The Journal Of Sexual Medicine

Pin Von Cindy Mungroo Auf Interesting To Me Anatomie

320 Male Pelvic Floor Dysfunction The Great Masquerader The Journal Of Sexual Medicine
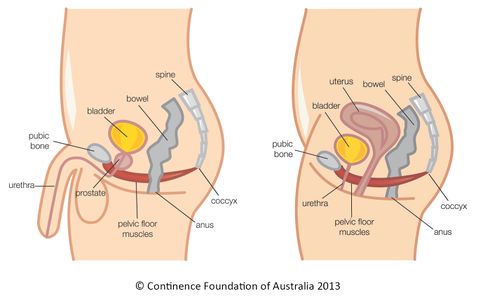
Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Physiopedia

1944 With The Serviceman S Readjustment Act Fdr Sets Up A Straight Male Veterans Only Welfare State Including Free College Ww1 Posters Military Kids Military

Part 1 Icd 10 For The Pelvic Health Patient Apta Pelvic Health
Herman Wallace Pelvic Rehabilitation Continuing Education The Pelvic Rehab Report Acupressure For Wholistic Pelvic Health Focus On Sanyinjiao Sp6 Acupoint Rachna Mehta

Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Illinois Chiropractic Society
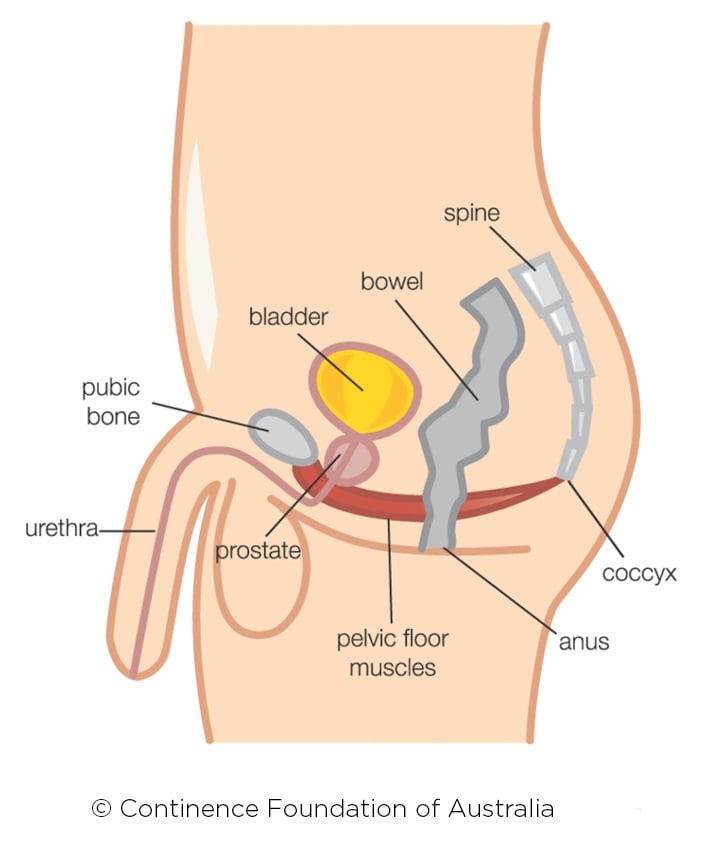
The Hypertonic Pelvic Floor Continence Foundation Of Australia

Myofascial Pain In Hysterectomy Patients Journal Of Minimally Invasive Gynecology
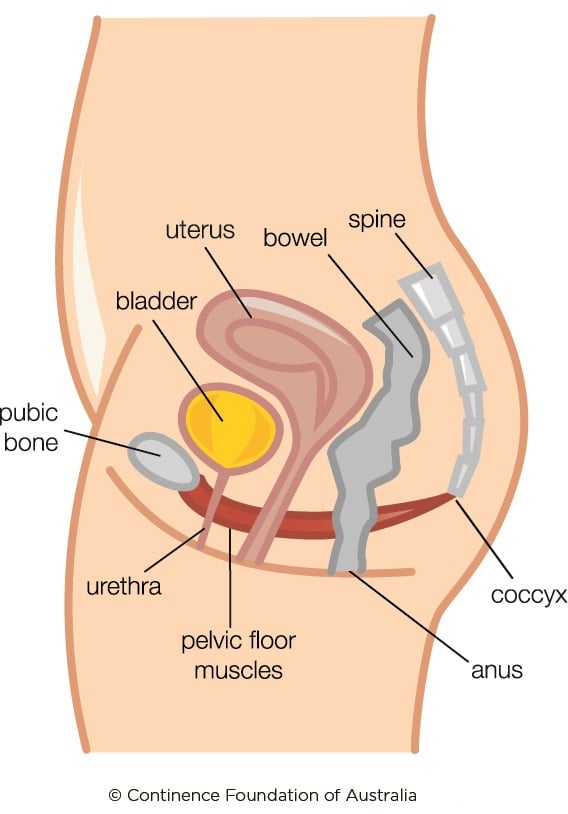
The Hypertonic Pelvic Floor Continence Foundation Of Australia

320 Male Pelvic Floor Dysfunction The Great Masquerader The Journal Of Sexual Medicine

Questions Surrounding The Optimal Time For Surgical Treatment Of Pelvic Organ Prolapse European Journal Of Obstetrics And Gynecology And Reproductive Biology



